Understanding the differences between KYB vs KYC

Table of Contents
This article discusses the nuances of KYB vs KYC, exploring their differences, importance, and implementation in the context of AML compliance.
As regulatory scrutiny intensifies, financial institutions must implement comprehensive due diligence measures to mitigate risks associated with money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes.
At the heart of these measures lie two critical processes: Know Your Customer (KYC) and Know Your Business (KYB). While both are essential components of a robust AML strategy, they serve distinct purposes and involve different methodologies.
KYB vs KYC: Key Differences
While KYC and KYB share the common goal of risk mitigation, they do differ in several integral aspects that make them both key considerations in an AML process:
- Scope of verification: KYC focuses on individual customers, while KYB addresses complex business entities.
- Complexity of due diligence: KYB generally involves more intricate investigations due to the layered nature of business structures and operations.
- Risk assessment methodologies: Business risk profiles often require more nuanced evaluation than individual customers.
- Frequency of reviews and updates: Business entities may require more frequent reviews due to changes in ownership, structure, or activity.
- Data sources and verification methods: KYB often relies on a broader range of data sources, including corporate registries, business credit reports, and industry-specific databases.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
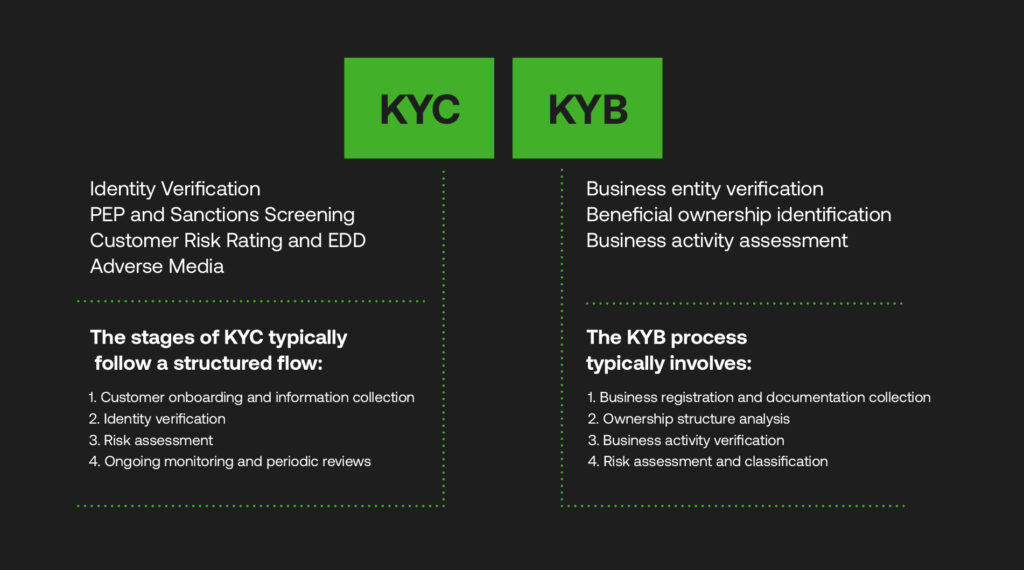
KYC is a process designed to verify the identity of individual customers and assess their risk profile. It encompasses several key components:
- Identity Verification: This involves collecting and validating basic customer information, such as name, address, date of birth, and government-issued identification documents.
- PEP and Sanctions Screening: Checking customers against lists of Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) and sanctioned individuals or entities to identify high-risk relationships.
- Customer Risk Rating and EDD: Assessing the customer’s risk level based on various factors and applying Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk customers involves more rigorous scrutiny and ongoing monitoring.
- Adverse Media: Conducting searches for negative news or information about the customer in various media sources to identify potential reputational or financial risks.
The stages of KYC typically follow a structured flow:
- Customer onboarding and information collection
- Identity verification
- Risk assessment
- Ongoing monitoring and periodic reviews
While KYC regulatory requirements vary by jurisdiction, they generally align with guidelines set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and local regulatory bodies.
Know Your Business (KYB)
KYB focuses on verifying and assessing the risk profile of business entities. Its major components include:
- Business entity verification: Confirming the legal existence and structure of the business.
- Beneficial ownership identification: Identifying and verifying the individuals who ultimately own or control the business.
- Business activity assessment: Understanding the nature of the business, its operations, and potential risks associated with its industry or geographical location.
The KYB process typically involves:
- Business registration and documentation collection
- Ownership structure analysis
- Business activity verification
- Risk assessment and classification
Regulatory requirements for KYB are often more complex than KYC, reflecting the intricate nature of business structures and ownership.
Importance of KYB and KYC in AML Compliance

- Risk mitigation: Identifying and managing potential risks associated with customers and business relationships.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting legal obligations and avoiding penalties for non-compliance.
- Fraud prevention: Detecting and deterring fraudulent activities through thorough due diligence.
- Reputation management: Protecting the institution’s reputation by avoiding association with illicit activities.
Best Practices for KYB and KYC Implementation
To optimise KYB and KYC, financial institutions should consider:
- Adopting a risk-based approach: Tailoring due diligence efforts based on the risk profile of customers and businesses.
- Leveraging technology: Harness the power of advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning to streamline your processes, drastically reduce errors, and free up valuable staff time for more complex tasks.
- Continuous monitoring: Establishing systems for ongoing monitoring and periodic customer and business information reviews.
- Staff training: Ensuring employees understand the importance of KYB and KYC and are equipped to implement processes effectively.
Challenges in Implementing KYB and KYC
Due to the thorough nature required of these processes, financial institutions face several challenges in implementing effective KYB and KYC:
- Data collection and management: Gathering accurate, up-to-date information can be challenging, especially for global businesses.
- Evolving regulatory landscape: Keeping pace with changing regulations across different jurisdictions.
- Technological limitations: Legacy systems may struggle to handle the complexity of modern KYB and KYC requirements.
- Resource allocation: Balancing the need for comprehensive due diligence with operational efficiency and cost considerations.
Future Trends in KYB & KYC
Given the nature of regulatory change currently underway, the future of KYB and KYC is likely to be shaped by multiple factors. The increased integration of AI and machine learning for more sophisticated risk assessment while adopting blockchain technology can allow for secure, decentralised identity verification.
Likewise, looking to RegTech solutions can streamline compliance processes while remaining cost-effective, where more collaborative efforts towards global standardisation of KYB and KYC requirements could make compliance more of a level playing field.
Key Takeaways
Financial institutions must stay agile by leveraging advanced technologies and best practices to optimise their KYB and KYC processes.
By doing so, FIs can meet compliance requirements and enhance their overall risk management capabilities, fostering trust and stability in the global financial ecosystem.
RelyComply offers end-to-end AML solutions driven by AI while efficiently integrating with legacy systems.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational purposes and reflects information correct at the time of publishing, which is subject to change and cannot guarantee accurate, timely or reliable information for use in future cases.


