How to avoid UK and SA anti-money laundering fines

Table of Contents
- The 2024-2025 AML penalty landscape: Record-breaking Fines
- Major UK AML fines (2024-2025)
- South African AML enforcement update (2024-2025)
- Anatomy of AML compliance failures – what goes wrong?
- The true cost of AML non-compliance in 2025
- Building a bulletproof AML compliance framework
- Key takeaways: your AML compliance action plan
Regulations around the world are tightening their grip, and financial institutions will face drastic measures for anti-money laundering (AML) compliance failures. Anti-money laundering fines in the UK and South Africa in 2025 have seen an upward trend – millions of pounds and rand in penalties that paint a worrying picture of how seriously compliance is taken in certain jurisdictions (and therefore major parts of the worldwide ecosystem).
When these fines can damage bottom lines and long-term reputations, AML compliance should be airtight even when regulatory scrutiny intensifies. Banks, insurers, fintechs, and other market entrants in the UK and South Africa are accountable under regional and global rules, where learning the main recommendations and past shortcomings can highlight where more attention should be paid in an AML strategy.
Here we’ll look into practical ways to avoid AML fines, from instilling greater controls from the onboarding and customer due diligence stages through to continuous record keeping, transaction monitoring and well-honed risk management frameworks. These current AML penalties identify the need for a cultural and technological change – one that can set up the UK and South Africa as future-proofed, exemplary AML compliance spearheads.
The 2024-2025 AML penalty landscape: Record-breaking Fines
No matter where we look across the financial world, the number of substantial fines dished out by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and other local watchdogs are sharply on the rise.
On a global scale, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) attempts to provide AML guidance, where the struggle to adhere to differing worldwide and regional standards for compliance still provides roadblocks for businesses under increased supervision and enforcement.
TD Bank, a leading lender in Canada, has set a new precedent for AML fines, agreeing to pay over $3 billion for allowing millions of laundered dollars through its system. To put this into context, the FCA’s total fines in the UK reached just over £176 million. This still indicated a sharp increase of 230% from the previous year, around £53 million.
Major UK AML fines (2024-2025)
While still dwarfed by Deutsche Bank AG’s record-breaking £163 million fine in 2017, so far the total number of fines issued in 2025 by the FCA is more than £34 million. This indicates some progress in the past decade, as well as improvements from 2024’s hefty year overall, but substantial fines display clear lapses in the financial crime prevention from various players in the financial sector.
Record-breaking FCA penalties
- Barclays: £42 million in 2025 for poor risk management and monitoring.
- Starling Bank: £28.9 million for failings related to sanctions screening.
- Monzo Bank: £21 million for repeated ignorance in onboarding high-risk customers between 2020 and 2022.
- Metro Bank: £16.7 million for inadequate controls to monitor £60 million in risky transactions.
Early 2025 AML enforcement actions
The FCA has indicated its strategy for the next 5 years, attempting to fight financial crime while rewarding growth for the good of consumers. In writing to CEOs at ‘Annex 1 firms’, the regulator is setting a high standard for identifying any lax financial crime controls, or failure to assess risk associated with their activities and that of their customers through resourcing and AML oversight.
The growing trend of FCA fines indicates the watchdog’s greater commitment to enforcement, with cooperative financial institutions called out for wrongdoing.
Common AML failure patterns in UK cases
As 2024/2025 AML compliance failures show, the biggest gaps for UK fintechs, banks and lenders tend to be poor controls for identifying high-risk customers – both at the know your customer (KYC) stage and through ongoing payment monitoring. Sanctions screening clearly has deficiencies too, indicative of systems not being aligned with the necessary watchlists to clamp down on sanctioned individuals.
South African AML enforcement update (2024-2025)
South Africa’s FATF greylisting in February 2023 threw its AML and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) enforcement under the spotlight, where some positive cooperative measures in completing 22 Action Items have seen a greater nationwide framework to hold institutions accountable.
SARB’s escalating AML penalty regime
Under FICA, the FIC has updated its penalty framework for non-compliance. This could reach up to R10 million for individuals (natural persons) and up to R50 million for entities (legal persons).
- Standard Bank: R13 million of administrative sanctions for non-compliance with provisions set out by the Financial Intelligence Centre (FIC).
- Old Mutual Life Assurance Company: R15.9 million for failures to comply with customer due diligence (CDD) and reporting obligations in the FIC Act (FICA).
- Bank of China (Johannesburg Branch): R30.5 million for failures in FICA requirements, including CDD and the submission of suspicious transaction reports (STRs).
- South Africa’s Prudential Authority also sanctioned Citibank, Bank of Taiwan, and HBZ Bank for non-compliance with risk management programs and recordkeeping obligations, with penalties reaching up to R9m
South Africa’s FATF greylisting impact
In order to seek removal from the FATF greylist, members from South Africa’s private and public sectors have increased their cooperation to adhere to the country’s Action Plan made in conjunction with the global regulator. Efforts have been well received, with South Africa’s potential delisting currently being audited by FATF.
FATF on-site inspection will determine the effectiveness and technical compliance of AML/CTF measures and whether a consistent approach is enacted across the board in regard to FATF’s 11 Immediate Outcomes – a “sustained political commitment”. This identifies the industry’s response to instil better technologically driven AML and cooperation between government bodies, regulators, and accountable institutions.
Key SARB enforcement trends 2024-2025
- Beneficial ownership verification: identifying the key controllers of companies or trusts in complex business structures.
- Enhanced due diligence: enforcing greater monitoring for high-risk entities.
- Cross-border transaction monitoring: identify any suspicious payments from jurisdictions with high-risk individuals and businesses, or lacking AML controls.
Anatomy of AML compliance failures – what goes wrong?
The analysis of major UK and South African AML penalties identifies consistent weaknesses that firms should address.

Customer Due Diligence breakdown
- Ultimate beneficial ownership (UBO) gaps: opaque business networks can mask the true identities of majority owners.
- Enhanced due diligence failures: legacy systems could miss behaviours indicative of high-risk customers or third parties need to be raised for increased investigation.
- Risk assessment inadequacies: a lack of risk-based technologies can waste time on legitimate customers and let high-risk entities slip through the net.
Transaction Monitoring system failures
- Technology gaps and false negatives: inefficient systems silo data and can cause manual errors, such as incorrectly reporting suspicious transactions.
- Threshold setting errors: a lack of AML controls to set risk thresholds can negate suspicious behaviours needed for timely reporting.
- Alert management deficiencies: unconsolidated platforms detach workflows needed to appropriately audit certain risk alerts.
Governance and training deficiencies
- Board-level oversight failures: a lack of care for AML sees limited attention granted to compliance budgets, resourcing and technology updates.
- Staff training inadequacies: undocumented protocols causes poor AML oversight across a business and understates the need for anti-fincrime controls.
- Compliance culture weaknesses: if still seen as a tickbox exercise, business-wide attitudes will not respect the severity of reputational damage.
The true cost of AML non-compliance in 2025
In the UK, the cost of compliance is estimated at £38.4 billion. Beyond dramatic monetary fines, regulatory enforcement actions create massive reputational damage and loss of customer trust. Insufficient AML measures can inflict severe financial and non-financial costs.
Directly, institutions will face upfront fines, as well as the remediation expenses that adhere to changing AML rules. This could also include the costs of legal counsel or AML consultations. Compliance resources will need to be reallocated accordingly, which could impact the budgets and time constraints needed to instil upgrades for regulatory technology (RegTech).
Indirectly, poor AML and reputational damage can significantly increase customer attrition and therefore cause roadblocks for business growth or market entry for startups.
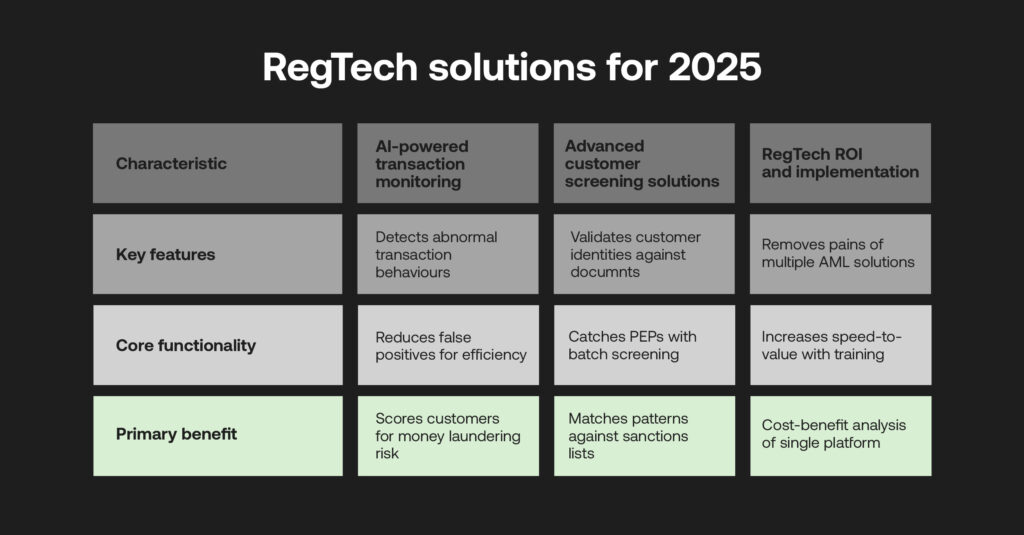
However, financial institutions can leverage RegTech to automate compliance processes and strengthen AML defences.
AI-powered Transaction Monitoring
- Machine learning capabilities: employ automated solutions to detect abnormal behaviours from millions of transactions.
- False positive reduction: increase the accuracy of finding suspicious behaviours to increase compliance team efficiency.
- Real-time risk scoring: instantly score customers for money laundering or sanctions risk upon onboarding with predictive analytics.
Advanced customer screening solutions
- Biometric verification: seamlessly validate customer identities against government documents with liveness checks.
- Automated PEP screening: use ongoing batch screening and real-time filtering of transactions against watchlists to catch PEPs.
- Sanctions list monitoring: match suspicious patterns and entities with integrated real-time assessment against trusted sanctions lists.
RegTech ROI and implementation
- Cost-benefit analysis: single platforms can remove the pains and expenses of integrating multiple AML compliance solutions.
- Deployment timelines: guided implementations, APIs, and ongoing training can increase speed-to-value.
Adopting RegTech allows firms to systemise compliance, reduce headcount costs and refocus human capital on high-value oversight and control testing.
Building a bulletproof AML compliance framework
Risk-based approach implementation
- Document methodologies for risk assessment.
- Profile customer risks according to bespoke business requirements.
- Establish approaches for ongoing monitoring for future-proofed AML.
Technology integration strategy
- Plan a flexible architecture in accordance with pre-existing systems.
- Utilise APIs to integrate AML data across siloed platforms for comprehensive AML workflows.
- Automate systems to compile compliance reports ready for audit.
Staff training and culture development
- Conduct role-specific training programs.
- Compile and document easily-accessible compliance culture metrics.
- Provide continuous education frameworks through events, roundtables and speaker series.
Key takeaways: your AML compliance action plan
Achieving consistent AML can take a few steps, from plotting procedures to partnering with RegTech providers.
Immediate Actions (0-30 days)
- Conduct an audit of AML compliance health, including data cleanliness.
- Adopt a framework to identify gaps in AML procedures
- Identify quick wins in existing AML systems.
Medium-term Strategy (30-90 days)
- Evaluate the capabilities of technologies and where integrations can be achieved.
- Develop a platform training program for employees.
- Update policy documents in line with jurisdictional regulatory needs.
Long-term Compliance Excellence (90+ days)
- Implement regular workshops and training to transform a positive AML compliance culture.
- Integrate systems and partner with RegTech providers.
- Continuously improve risk assessment capabilities for changing requirements, emerging technologies and threats.
By investing in the right AML software and understanding past compliance failures, firms can transform processes to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Arrange a demo with our team today to see how cutting-edge RegTech solutions can drive agility and efficiency to achieve exemplary AML in the tricky compliance landscape.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational purposes and reflects information correct at the time of publishing, which is subject to change and cannot guarantee accurate, timely or reliable information for use in future cases.


